Diabetic Eye Exams
What are the importance of regular Diabetic Eye Exams for individuals with diabetes? How can these exams help safeguard your vision and prevent serious eye complications? In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the critical role of Diabetic Eye Exams in maintaining eye health and preserving your eyesight.
The Importance of Diabetic Eye Exams
Living with diabetes can present a unique set of challenges when it comes to maintaining overall health, and the eyes are no exception. Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing various eye-related complications, including diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and cataracts. These conditions, if left unchecked, can lead to permanent vision impairment and even blindness.
The key to managing these risks lies in regular Diabetic Eye Exams. These comprehensive eye examinations, performed by qualified eye care professionals, are specifically designed to detect and monitor any changes or damage to the eyes that may be caused by diabetes. By staying proactive with these exams, individuals with diabetes can take a significant step towards preserving their sight and preventing vision loss.
Understanding Diabetic Eye Conditions
Diabetes can have a profound impact on the eyes, leading to the development of several eye-related complications. Let’s explore some of the most common conditions that can be detected and managed through Diabetic Eye Exams.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the most prevalent eye conditions associated with diabetes. This condition occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the small blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, these blood vessels can become blocked, leak, or form new, abnormal vessels, leading to vision impairment and potential blindness.
Macular Edema
Another common eye condition in individuals with diabetes is macular edema. This occurs when fluid and protein accumulate within the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. This buildup of fluid can cause the macula to swell and distort vision, making it difficult to perform tasks like reading or driving.
Cataracts
Individuals with diabetes are also at an increased risk of developing cataracts, a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes clouded, making it more difficult to see. This can lead to blurred or hazy vision, glare, and difficulty seeing at night.
The Role of Diabetic Eye Exams
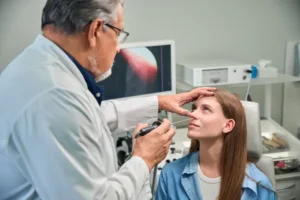
Diabetic Eye Exams play a crucial role in the early detection and management of these eye-related conditions. These comprehensive examinations involve a series of tests and procedures that allow eye care professionals to assess the health of the eyes and identify any potential issues.
During a Diabetic Eye Exam, the eye care professional will typically perform the following:
- Visual acuity test: This measures your ability to see clearly at various distances.
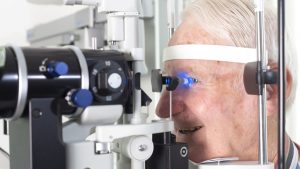
- Dilated eye exam: The eye care professional will use eye drops to dilate your pupils, allowing them to examine the inside of your eyes more thoroughly.
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside your eyes, which can indicate the presence of glaucoma.
- Retinal exam: The eye care professional will use a specialized camera to take images of the back of your eyes, including the retina, to check for signs of diabetic retinopathy and other conditions.
By undergoing regular Diabetic Eye Exams, individuals with diabetes can ensure that any eye-related issues are detected and addressed in a timely manner. Early intervention is crucial in preventing vision loss and maintaining optimal eye health.
Here you like The Role of Eye Exams in Maintaining Healthy Vision: Advice from Hindsight Eye Care in Oxford
The Frequency of Diabetic Eye Exams
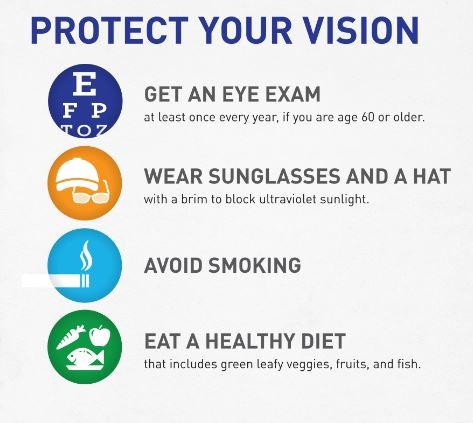
The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes have a comprehensive Diabetic Eye Exam at least once a year. However, the frequency of these exams may vary depending on the individual’s overall health, the duration of their diabetes, and the presence of any existing eye-related conditions.
For example, individuals with newly diagnosed diabetes or those with well-controlled blood sugar levels may only need a Diabetic Eye Exam once a year. On the other hand, those with a longer history of diabetes or those who have already developed eye complications may require more frequent exams, such as every six months or as recommended by their eye care professional.
It’s important to work closely with your eye care provider to determine the appropriate frequency of Diabetic Eye Exams based on your individual circumstances and risk factors.
Preparing for a Diabetic Eye Exam
Before your Diabetic Eye Exam, there are a few steps you can take to ensure that the examination goes as smoothly as possible:
Gather your medical history: Be prepared to provide your eye care professional with information about your diabetes, including when you were diagnosed, your current treatment plan, and any complications you may have experienced.
Bring a list of your medications: Make sure to bring a list of all the medications you are currently taking, including any over-the-counter supplements or vitamins.
Inform your eye care provider: Let your eye care professional know about any changes in your vision or any eye-related symptoms you may be experiencing.
Expect dilation: As mentioned earlier, your pupils will likely be dilated during the exam to allow for a more thorough examination of the inside of your eyes. This may cause your vision to be blurry for a few hours after the exam, so be prepared to have someone assist you with transportation if necessary.
By being proactive and preparing for your Diabetic Eye Exam, you can ensure that your eye care provider has all the information they need to provide you with the best possible care and support.
Treating Eye Conditions Identified During Diabetic Eye Exams
If your Diabetic Eye Exam reveals the presence of any eye-related conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, or cataracts, your eye care professional will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment options may include:
Medication: Your eye care professional may prescribe eye drops or other medications to help manage the condition and prevent further vision loss.
Laser therapy: In cases of diabetic retinopathy or macular edema, laser treatment may be used to seal leaking blood vessels or prevent the growth of new, abnormal vessels.
Surgical interventions: For more advanced or severe eye conditions, such as advanced diabetic retinopathy or cataracts, surgical procedures may be recommended to restore or preserve vision.
It’s important to follow your eye care provider’s recommendations and adhere to your treatment plan to ensure the best possible outcome for your eye health.
The Long-Term Benefits of Regular Diabetic Eye Exams
By making Diabetic Eye Exams a regular part of your healthcare routine, you can proactively protect your vision and prevent vision loss. These comprehensive exams can help:
Detect eye conditions early: Diabetic Eye Exams allow for the early detection of eye-related conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy and macular edema, enabling timely intervention and management.
Monitor existing conditions: If you have already been diagnosed with an eye condition, regular Diabetic Eye Exams can help your eye care provider monitor the progression of the condition and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Prevent vision loss: Diabetic Eye Exams can help you avoid or slow the progression of vision loss by addressing eye-related conditions in a timely manner, allowing you to maintain your independence and quality of life.
Provide peace of mind: Knowing that your eyes are being regularly checked and cared for can reassure you and help you feel more in control of your overall health.
Incorporating Diabetic Eye Exams into your healthcare routine is a simple yet powerful step you can take to safeguard your vision and preserve your long-term eye health.
FAQs
How often should I have a Diabetic Eye Exam?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes have a comprehensive Diabetic Eye Exam at least once a year. However, the frequency may vary depending on your individual circumstances and the presence of any existing eye-related conditions.
What can Diabetic Eye Exams detect?
Diabetic Eye Exams can detect a range of eye-related conditions, including diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and cataracts, which are more common in individuals with diabetes.
How do Diabetic Eye Exams help prevent vision loss?
By identifying and addressing eye-related conditions early, Diabetic Eye Exams allow for timely intervention and management, which can help prevent or slow the progression of vision loss.
What should I do to prepare for a Diabetic Eye Exam?
To prepare for a Diabetic Eye Exam, gather your medical history, bring a list of your medications, and be ready to inform your eye care provider of any changes in your vision or eye-related symptoms.
How are eye conditions treated after being identified during a Diabetic Eye Exam?
Treatment options may include medication, laser therapy, or surgical interventions, depending on the specific condition and its severity. Your eye care provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.